Online Gambling Access Around The World
Over 50 percent of the world's population is banned from accessing online casinos in their own countries. On the other hand, over 60 countries around the world license online gambling which allows their citizens to bet. This is according to new research. It found that the situation in terms of gambling availability varies greatly from country to country.
In some countries casinos of any type, either land-based or online, are banned, while in others they are allowed. In those countries where casinos are allowed some ban local companies from operating a casino, while foreign firms continue to trade. Quirky rules also exist. For example, some countries ban their citizens from casinos but allow visitors play, and in at least one country casinos are only available to people who earn a high enough salary.
The research was carried by the KeyToCasino research team. The authors analyzed the gambling laws in 225 countries and territories by looking at a range of sources in 46 different languages. The sources in each of the countries where the information was collated varied:
- In 83 percent of the countries, the information on casinos was available on official, local sources such as government run websites.
- In 12 percent of the countries, the information obtained for the research came from reputable local sources, but they were not official websites. Examples include major local newspapers and the websites of law firms.
- In the remaining five percent the information was only available from non-local or less reliable sources.
Thus, for the 95 percent of the countries, or 98 percent of the world population, the information came from local, reputable sources. All of the underlying data and the sources are available on the following page. The report is based on the data as of March 1st, 2015. The tables, however, are constantly updated to reflect the current position of casino and gambling availability around the world.
Some Background First
In conducting the research, KeyToCasino team wanted to give a snapshot of the state of global regulations on casinos, and the different barriers faced by players around the world.
Regulations governing gambling have been enforced by governments and leaders for almost as long as gambling has existed. This goes all the way back to ancient Chinese and Roman societies. The modern casino, as we know it today, has its origins in the 17th century Europe. It was called the Il Ridotto and it was located in Venice in Italy. It opened in 1638 and facilitated gambling during the carnival season, under control by the Italian government.
Today almost every country in the world has its own gambling laws, although in some places gambling is not regulated at all. In many countries the industry is controlled through licensing and supervision, but there are some places where gambling is completely forbidden.
The Findings
Land-based Casinos
Land-based casinos have been in existence longer than online casinos, so in most countries the laws regarding their operation are much more established. Of the countries researched, 74 apply restrictions to land-based casinos:
- 51 ban them altogether.
- Six countries ban their own citizens from playing, but allow foreign visitors.
- 17 countries restrict casinos to certain cities, or specified localities.
That leaves 151 countries (or 67 percent) where casinos are fully legal. But this doesn't tell the whole story as only 47 percent of the world's population can access the casinos in their own countries.

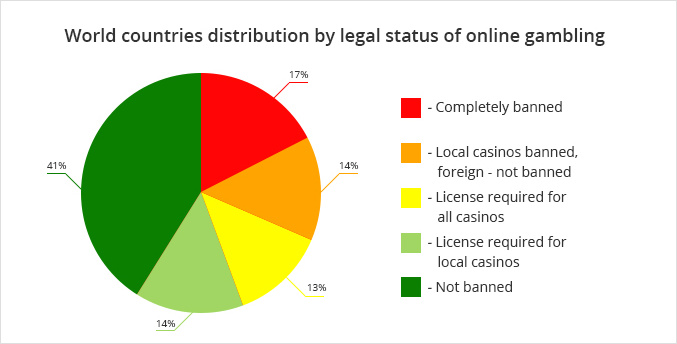
Online Casinos
The situation with online casinos is more mixed. This is because of the way countries treat local operators and foreign operators, which in some cases is very different. Some form of ban is in place for 56 percent of the world's population.
- 39 countries ban online casinos completely.
- 32 countries ban local operators from running casinos, but many that are run by foreign countries still take bets. The reasons for this anomaly are varied, including the fact that some countries do not have the resources or influences to stop foreign companies from offering online gambling services.
- 61 countries allow casinos to operate under license. In half of these countries the licensing requirement is strictly enforced only on local casinos. Foreign operators often take bets, even when they don’t have a license. As in the previous point, these countries are not willing or not able to stop foreign companies from offering gambling services.
- 93 countries do not explicitly ban online casinos, and they don't license them either.
Comparison
These data are useful but it is also helpful to look at how countries with land-based casino bans handle online casinos, and vice-versa. There are 168 countries which allow their citizens to play in land-based casinos, although some only allow casinos in certain parts of the country. How do those countries deal with online casinos?
- 27 countries ban online casinos, despite allowing land-based versions.
- 60 countries operate some form of online casino regulation.
- 81 countries have no ban.
Citizens who live in 57 countries around the world do not have the facility to bet in land-based casinos. Can they bet online?
- In 44 countries they cannot because both land-based and online casinos are banned.
- In 13 countries the population is allowed to play in online casinos, even though land-based casinos are banned. This is because no explicit online casino ban is in place, or because online operators are allowed despite the fact that land-based operators are prohibited.

On the Players' Side of the Table
In 132 countries where online gambling operators are banned or restricted , what happens to the ordinary people who place bets online?
- In 92 countries, nothing happens as no penalties are imposed.
- 15 countries impose an administrative penalty on players.
- 25 countries impose a criminal penalty.
Some countries make an additional effort to prevent their citizens from placing illegal online bets.
- 36 countries require internet service providers to block access to some or all casino websites.
- 18 countries order banks to block the financial transactions of casinos.
How the Casinos Operate
The laws and regulations do not always reflect the reality of how certain casinos operate. Some casinos claim to operate in countries where there are restrictions, while other casinos voluntarily restrict access to citizens of certain countries, even though there is no legal reason for doing so. Most do this for marketing or business reasons.
The researchers conducted this part of the project by getting 655 online casinos to give them a list of countries where their services are restricted either by local laws, or voluntary restriction.
The results are interesting:
- On average, 24% of online casinos restrict access to players who live in a country where a license is required to operate a casino.
- On average, 22% of casinos restrict access to players who live in countries where bans or restrictions are in place.
- On average, 16% of casinos restrict access to players even when they live in countries where foreign companies can operate.
- On average, 14% of casinos restrict access to players who live in countries where local casinos are licensed but foreign companies can operate.
- On average, 14% of casinos restrict access to players despite the fact that they live in countries that have no online gambling restrictions.

So what countries are included most often on the casinos' banned lists? The United States is at the top of the table followed by France and Israel. People who live in the United States are banned from playing in 72 percent of the world’s online casinos. In France and Israel, the percentage is 70 and 54, respectively.

At the other end of the scale there are countries that casinos restrict the least. Only seven percent of the online casinos restrict Iceland citizens from playing. People who live in New Zealand, Austria, Argentina and Sweden are also welcomed by the vast majority of the online casinos.

Gambling Availability Score
To help individuals to navigate this complex picture, KeyToCasino combined all research results discussed in this document and scored every country. The resulting number was called Gambling Availability Score.
Each country can score a maximum of 1000 points. The scoring is based on six different factors:
- 500 points allocated based on the percentage of online casinos that allow citizens from the country to play.
- 100 points based on the country’s law regarding land-based casinos.
- 100 points based on the country’s law regarding online casino operators.
- 100 points based on the existence and severity of penalties that players face.
- 100 points based on whether internet service providers in the country block access to casinos.
- 100 points based on whether the online gambling related financial transactions are blocked by the country.
When all of this is collated together it provides a combination of the position of a country’s government towards online gambling and the attitude of the online casinos towards that country.
According to the Gambling Availability Score, the United States is the worst country for online gamblers to live in. It scored just 311 points out of 1,000. Iran and France are the next two worst, scoring 407 and 412 respectively.

The countries that get the best scores are Chile, Andorra, and Venezuela. They each score 960 out of a possible 1,000. Your country's current score is available on the following page.
It should be noted that the score does not take into account the internet accessibility in each of the countries. Many of the countries in the top 10 have low rates of internet access. This means that while their citizens might have good access to online gambling, not many of them probably do because of their limited access to the internet. The Gambling Availability Score reflects opportunity and convenience in regards to online gambling, rather than the casino usage rate.
Did you know that...
Here are some interesting facts that the authors have found during their legal research:
- In some countries, casinos are allowed on ships but not on land. Examples include Russia, Thailand, Israel, Japan, or the USA.
- In Israel, gamblers only have to be in a place that offers prohibited games to get them into trouble with the police, i.e. the police have no obligation to prove that the person was actually playing.
- In some middle-eastern countries, there is no gambling restriction on the books, but it is completely banned due to prohibition in Quran (verses 5:90–91).
- In Belarus, citizens are allowed to go to casinos but they can ask the government to formally ban them.
- In Faroe Islands, one cannot import any kinds of slot machines even for the private use or collection purposes.
- In Turks & Caicos, only those earning more than $75,000 / year are allowed to gamble in casinos.
- In Norway, land-based casinos are banned, but online casinos are licensed and regulated.
- Libya treats gambling under the same set of laws that it treats sorcery and witchcraft.
The information, figures and materials included in this document and this research are available for general use. Publication of the research and the figures is allowed, provided a link to the KeyToCasino website is included in the publication.




